Custom Lobes
Extend OctoMY™ with custom processing modules
Custom Lobes
Learn how to create custom Lobes to extend OctoMY™'s capabilities with specialized processing, AI integration, or custom hardware support.
Pro Tip
Before creating a custom lobe, check if a built-in lobe already supports your needs. Custom lobes are powerful but require C++ development and rebuild cycles.
What are Lobes?
Lobes are modular processing components that extend OctoMY™:
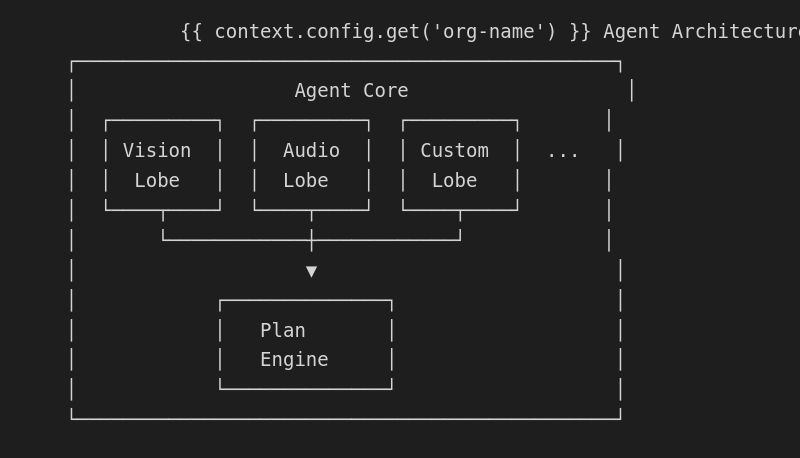
Built-in lobes
| Lobe | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Vision | Camera processing, object detection |
| Audio | Sound input/output, speech |
| GPS | Location tracking |
| Sensors | Hardware sensor abstraction |
| Comms | Network communication |
Why custom lobes?
- Custom hardware - Support specialized sensors/actuators
- AI integration - Add ML models, LLM, or computer vision
- Protocols - Implement proprietary communication
- Processing - Custom data processing pipelines
Did You Know?
The name "Lobe" comes from brain anatomy - just as brain lobes handle specialized functions (vision, language, motor control), OctoMY™ Lobes handle specialized robot functions.
Lobe architecture
Lobe interface
All Lobes implement the ILobe interface:
class ILobe : public QObject {
Q_OBJECT
public:
// Lifecycle
virtual QString name() const = 0;
virtual bool initialize() = 0;
virtual void shutdown() = 0;
// Processing
virtual void process() = 0;
// Status
virtual LobeStatus status() const = 0;
signals:
void statusChanged(LobeStatus status);
void dataReady(const QVariantMap &data);
};
Lobe lifecycle

Step 1: Create lobe structure
File structure
src/libs/liblobes/
├── lobes/
│ └── myCustomLobe/
│ ├── MyCustomLobe.hpp
│ ├── MyCustomLobe.cpp
│ └── MyCustomLobe.qbs
└── lobes.qbs
Header file
// MyCustomLobe.hpp
#pragma once
#include "lobes/ILobe.hpp"
#include <QObject>
#include <QTimer>
class MyCustomLobe : public ILobe {
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit MyCustomLobe(QObject *parent = nullptr);
~MyCustomLobe() override;
// ILobe interface
QString name() const override;
bool initialize() override;
void shutdown() override;
void process() override;
LobeStatus status() const override;
// Custom methods
double getCustomValue() const;
void setParameter(const QString &key, const QVariant &value);
signals:
void customDataReady(double value);
private slots:
void onTimerTick();
private:
QTimer *mProcessTimer{nullptr};
LobeStatus mStatus{LobeStatus::Uninitialized};
double mCustomValue{0.0};
// Configuration
int mUpdateRate{20}; // Hz
};
Implementation
// MyCustomLobe.cpp
#include "MyCustomLobe.hpp"
#include <QDebug>
MyCustomLobe::MyCustomLobe(QObject *parent)
: ILobe(parent)
, mProcessTimer(new QTimer(this))
{
connect(mProcessTimer, &QTimer::timeout,
this, &MyCustomLobe::onTimerTick);
}
MyCustomLobe::~MyCustomLobe() {
shutdown();
}
QString MyCustomLobe::name() const {
return QStringLiteral("MyCustomLobe");
}
bool MyCustomLobe::initialize() {
qDebug() << "Initializing MyCustomLobe";
// Initialize resources
// Connect to hardware, load models, etc.
mStatus = LobeStatus::Initialized;
emit statusChanged(mStatus);
// Start processing
mProcessTimer->start(1000 / mUpdateRate);
mStatus = LobeStatus::Running;
emit statusChanged(mStatus);
return true;
}
void MyCustomLobe::shutdown() {
if (mStatus == LobeStatus::Running) {
mProcessTimer->stop();
// Clean up resources
mStatus = LobeStatus::Stopped;
emit statusChanged(mStatus);
}
}
void MyCustomLobe::process() {
// Called each timer tick
// Do your processing here
// Example: generate some data
mCustomValue = qrand() / (double)RAND_MAX * 100.0;
// Emit data for Plans to consume
emit customDataReady(mCustomValue);
QVariantMap data;
data["value"] = mCustomValue;
data["timestamp"] = QDateTime::currentMSecsSinceEpoch();
emit dataReady(data);
}
void MyCustomLobe::onTimerTick() {
process();
}
LobeStatus MyCustomLobe::status() const {
return mStatus;
}
double MyCustomLobe::getCustomValue() const {
return mCustomValue;
}
void MyCustomLobe::setParameter(const QString &key, const QVariant &value) {
if (key == "updateRate") {
mUpdateRate = value.toInt();
if (mProcessTimer->isActive()) {
mProcessTimer->setInterval(1000 / mUpdateRate);
}
}
}
Security Consideration
Custom lobes have full access to the Agent's resources. Be careful when loading external models or connecting to network services. Validate all inputs and handle errors gracefully.
Step 2: Register the lobe
Lobe registry
Register your Lobe with the Agent:
// In LobeFactory.cpp
#include "lobes/myCustomLobe/MyCustomLobe.hpp"
ILobe* LobeFactory::createLobe(const QString &name) {
if (name == "MyCustomLobe") {
return new MyCustomLobe();
}
// ... other lobes
return nullptr;
}
QStringList LobeFactory::availableLobes() {
return {
"VisionLobe",
"AudioLobe",
"MyCustomLobe", // Add here
// ...
};
}
Configuration
Enable in Agent configuration:
{
"lobes": {
"MyCustomLobe": {
"enabled": true,
"updateRate": 30,
"customParam": "value"
}
}
}
Step 3: Access from plans
OPAL integration
Access your Lobe from OPAL plans:
plan UseCustomLobe {
loop {
// Read data from custom lobe
var value = lobes.MyCustomLobe.value
log("Custom value: " + value)
if value > 50 {
do_something()
}
delay(100)
}
}
Event handling
React to Lobe events:
plan ReactToLobe {
// Called when lobe emits data
on lobe_data("MyCustomLobe") { data ->
log("Got data: " + data.value)
process_data(data)
}
loop {
// Normal plan logic
delay(100)
}
}
Example: AI vision lobe
A Lobe that uses OpenCV for object detection:
Pro Tip
OpenCV's Haar cascades are fast but not as accurate as modern deep learning. For production face detection, consider using dlib or a DNN-based approach instead.
// AiVisionLobe.hpp
#pragma once
#include "lobes/ILobe.hpp"
#include <QObject>
#include <QImage>
class AiVisionLobe : public ILobe {
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit AiVisionLobe(QObject *parent = nullptr);
QString name() const override { return "AiVision"; }
bool initialize() override;
void shutdown() override;
void process() override;
LobeStatus status() const override;
// Vision methods
QList<DetectedObject> detectObjects(const QImage &frame);
signals:
void objectsDetected(const QList<DetectedObject> &objects);
private:
void processFrame(const QImage &frame);
cv::CascadeClassifier mClassifier;
bool mInitialized{false};
};
// AiVisionLobe.cpp
#include "AiVisionLobe.hpp"
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
bool AiVisionLobe::initialize() {
// Load Haar cascade for face detection
QString cascadePath = ":/cascades/haarcascade_frontalface.xml";
if (!mClassifier.load(cascadePath.toStdString())) {
qWarning() << "Failed to load cascade";
return false;
}
mInitialized = true;
return true;
}
void AiVisionLobe::process() {
// Get frame from camera (via CameraLobe or direct)
QImage frame = getCameraFrame();
if (!frame.isNull()) {
processFrame(frame);
}
}
void AiVisionLobe::processFrame(const QImage &frame) {
// Convert to OpenCV format
cv::Mat cvFrame = qImageToCvMat(frame);
cv::Mat gray;
cv::cvtColor(cvFrame, gray, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
// Detect faces
std::vector<cv::Rect> faces;
mClassifier.detectMultiScale(gray, faces, 1.1, 3);
// Convert to DetectedObject list
QList<DetectedObject> objects;
for (const auto &face : faces) {
DetectedObject obj;
obj.type = "face";
obj.rect = QRect(face.x, face.y, face.width, face.height);
obj.confidence = 1.0;
objects.append(obj);
}
emit objectsDetected(objects);
}
Use in Plans
plan FaceTracker {
on lobe_data("AiVision") { data ->
if data.objects.length > 0 {
var face = data.objects[0]
var center_x = face.rect.x + face.rect.width / 2
// Track face with pan servo
var frame_center = 320 // Assuming 640px width
var error = center_x - frame_center
servos.pan = servos.pan - error * 0.1
}
}
loop {
delay(50)
}
}
Example: LLM integration lobe
Integrate an LLM for natural language understanding:
// LlmLobe.hpp
#pragma once
#include "lobes/ILobe.hpp"
class LlmLobe : public ILobe {
Q_OBJECT
public:
QString name() const override { return "LLM"; }
bool initialize() override;
void process() override;
// Query the LLM
Q_INVOKABLE QString query(const QString &prompt);
Q_INVOKABLE void queryAsync(const QString &prompt);
signals:
void responseReady(const QString &response);
private:
QNetworkAccessManager *mNetwork{nullptr};
QString mApiKey;
QString mEndpoint;
};
// LlmLobe.cpp
void LlmLobe::queryAsync(const QString &prompt) {
QJsonObject request;
request["model"] = "gpt-4";
request["messages"] = QJsonArray{
QJsonObject{
{"role", "system"},
{"content", "You are a robot assistant. Respond concisely."}
},
QJsonObject{
{"role", "user"},
{"content", prompt}
}
};
QNetworkRequest req(QUrl(mEndpoint));
req.setHeader(QNetworkRequest::ContentTypeHeader, "application/json");
req.setRawHeader("Authorization", ("Bearer " + mApiKey).toUtf8());
auto *reply = mNetwork->post(req, QJsonDocument(request).toJson());
connect(reply, &QNetworkReply::finished, [this, reply]() {
auto response = QJsonDocument::fromJson(reply->readAll());
QString text = response["choices"][0]["message"]["content"].toString();
emit responseReady(text);
reply->deleteLater();
});
}
Use in Plans
plan VoiceAssistant {
on voice_command(cmd) {
// Send to LLM
lobes.LLM.queryAsync(cmd)
}
on lobe_data("LLM") { response ->
// Speak the response
speak(response.text)
// Parse for actions
if response.text.contains("turn left") {
turn_left()
}
}
}
Example: Custom sensor lobe
Support a custom sensor protocol:
// LidarLobe.hpp
class LidarLobe : public ILobe {
Q_OBJECT
public:
QString name() const override { return "Lidar"; }
bool initialize() override;
void process() override;
// Get scan data
QVector<float> getScanDistances() const;
float getDistanceAtAngle(float angle) const;
signals:
void scanComplete(const QVector<float> &distances);
private:
void parseScanData(const QByteArray &data);
QSerialPort *mSerial{nullptr};
QVector<float> mDistances; // 360 readings
};
Use in Plans
plan LidarNavigation {
loop {
var scan = lobes.Lidar.distances
// Find closest obstacle
var min_distance = 9999
var min_angle = 0
for i in 0..360 {
if scan[i] < min_distance {
min_distance = scan[i]
min_angle = i
}
}
if min_distance < 50 {
// Obstacle nearby
avoid_direction(min_angle)
}
delay(100)
}
}
Build configuration
Qbs build file
// MyCustomLobe.qbs
import qbs
StaticLibrary {
name: "MyCustomLobe"
Depends { name: "Qt.core" }
Depends { name: "liblobes" }
files: [
"MyCustomLobe.cpp",
"MyCustomLobe.hpp",
]
Export {
Depends { name: "Qt.core" }
}
}
Dependencies
Add external dependencies as needed:
// For OpenCV
Depends { name: "opencv" }
// For network
Depends { name: "Qt.network" }
// For serial
Depends { name: "Qt.serialport" }
Best practices
- Thread safety - Use signals/slots for cross-thread communication
- Resource cleanup - Always clean up in
shutdown() - Error handling - Emit status changes on errors
- Configuration - Support runtime parameter changes
- Documentation - Document available data and methods
- Testing - Create unit tests for Lobe logic
Troubleshooting
Lobe not loading
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Not registered | Add to LobeFactory |
| Build error | Check dependencies in qbs |
| Initialization fails | Check initialize() return |
Data not reaching plans
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Signal not emitted | Call emit dataReady() |
| Wrong data format | Use QVariantMap correctly |
| Not connected | Verify signal connections |
Next steps
- Multiple Agents - Multi-Agent Setup
- Central Hub - Hub Setup
- Lobe reference - Lobes Reference