Create a Plan
Write autonomous behavior scripts in OPAL
Create a Plan
Create Plans to define autonomous behaviors for your OctoMY™ Agent using OPAL (OctoMY™ Programming and Automation Language).
Pro Tip
Start with the obstacle avoider example - it covers all the basics: sensor reading, motor control, conditionals, and timing. Modify it incrementally to learn how each part works before writing your own plan from scratch.
What is a plan?
A Plan is a behavior script that tells your Agent what to do autonomously. Plans can:
- React to sensors - Respond to distance, temperature, light
- Control actuators - Move servos, drive motors
- Make decisions - If/else logic, state machines
- Handle events - Timer triggers, remote commands
- Run in background - Continuous autonomous operation
Prerequisites
- Agent running with hardware configured
- Familiarity with basic programming concepts
- Understanding of your Agent's sensors and actuators
Step 1: Open the plan editor
On the Agent:
- Open ☰ Menu → Plans
- Tap [New Plan]
Step 2: Name your plan
Give your Plan a descriptive name:

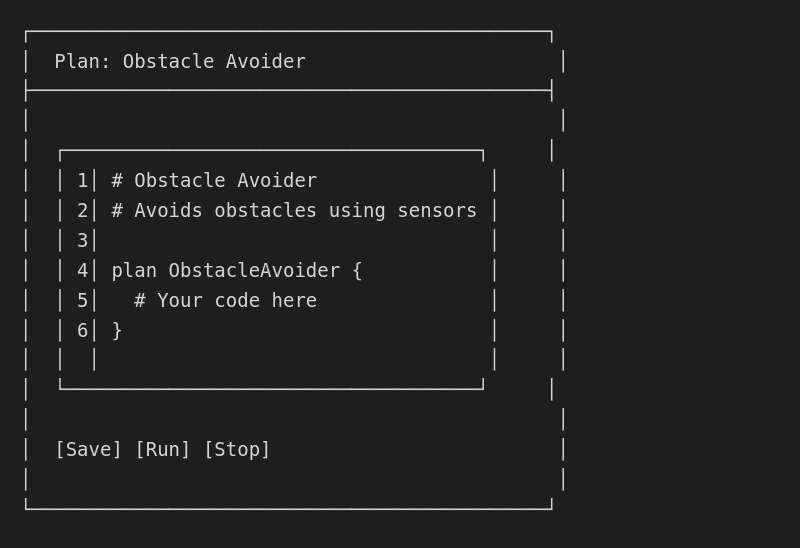
Step 3: Write OPAL code
The Plan Editor opens with a template:
OPAL basics
Plan structure
Every Plan follows this structure:
# Comment describing the plan
plan PlanName {
# Variables
var speed = 50
# Initialization (runs once at start)
init {
log("Plan started")
}
# Main loop (runs continuously)
loop {
# Your behavior logic
}
# Cleanup (runs when plan stops)
cleanup {
stop_motors()
}
}
Variables
# Numbers
var speed = 100
var threshold = 30.5
# Booleans
var enabled = true
var obstacle_detected = false
# Strings
var state = "searching"
Sensor access
# Read sensor values
var distance = sensors.distance.front
var temperature = sensors.temperature
var battery = sensors.battery.level
var heading = sensors.imu.heading
Actuator control
# Motor control
motors.left.speed = 50 # -100 to 100
motors.right.speed = 50
# Servo control
servos.arm.angle = 90 # Degrees
servos.gripper.angle = 45
# Helper functions
drive(50, 50) # Left, right speeds
turn_left(30) # Turn at speed
turn_right(30)
stop_motors()
Conditionals
if distance < 30 {
# Too close, back up
drive(-50, -50)
} else if distance < 60 {
# Getting close, slow down
drive(25, 25)
} else {
# Clear path, full speed
drive(100, 100)
}
Loops
# While loop
while enabled {
check_sensors()
delay(100)
}
# For loop
for i in range(5) {
blink_led()
delay(500)
}
Example: Simple obstacle avoider
# Obstacle Avoider
# Drives forward, turns when obstacle detected
plan ObstacleAvoider {
var safe_distance = 40 # cm
var drive_speed = 60
var turn_speed = 40
init {
log("Obstacle avoider starting")
face.set_expression("happy")
}
loop {
var front = sensors.distance.front
if front < safe_distance {
# Obstacle detected - turn away
face.set_expression("surprised")
log("Obstacle at " + front + "cm")
# Back up a bit
drive(-30, -30)
delay(300)
# Turn right
drive(turn_speed, -turn_speed)
delay(500)
face.set_expression("happy")
} else {
# Path clear - drive forward
drive(drive_speed, drive_speed)
}
delay(50) # 20Hz update rate
}
cleanup {
stop_motors()
face.set_expression("neutral")
log("Obstacle avoider stopped")
}
}
Example: Line follower
# Line Follower
# Follows a dark line on light surface
plan LineFollower {
var base_speed = 50
var turn_factor = 0.8
var line_threshold = 500
init {
log("Line follower starting")
}
loop {
var left_sensor = sensors.line.left
var right_sensor = sensors.line.right
var left_on_line = left_sensor < line_threshold
var right_on_line = right_sensor < line_threshold
if left_on_line and right_on_line {
# On the line - go straight
drive(base_speed, base_speed)
} else if left_on_line {
# Line is to the left - turn left
drive(base_speed * turn_factor, base_speed)
} else if right_on_line {
# Line is to the right - turn right
drive(base_speed, base_speed * turn_factor)
} else {
# Lost the line - search
drive(base_speed / 2, -base_speed / 2)
}
delay(20)
}
cleanup {
stop_motors()
}
}
Example: Patrol behavior
# Patrol
# Moves between waypoints, pausing at each
plan Patrol {
var waypoints = [
{x: 0, angle: 0},
{x: 0, angle: 90},
{x: 0, angle: 180},
{x: 0, angle: 270}
]
var current_waypoint = 0
var pause_time = 3000 # ms
init {
log("Patrol starting")
}
loop {
var target = waypoints[current_waypoint]
# Turn to target heading
turn_to_heading(target.angle)
# Move forward for a bit
drive(50, 50)
delay(2000)
stop_motors()
# Pause and look around
log("Reached waypoint " + current_waypoint)
look_around()
delay(pause_time)
# Next waypoint
current_waypoint = (current_waypoint + 1) % len(waypoints)
}
func turn_to_heading(target) {
var current = sensors.imu.heading
var diff = target - current
while abs(diff) > 5 {
if diff > 0 {
drive(30, -30)
} else {
drive(-30, 30)
}
delay(50)
current = sensors.imu.heading
diff = target - current
}
stop_motors()
}
func look_around() {
servos.head_pan.angle = 45
delay(500)
servos.head_pan.angle = 135
delay(500)
servos.head_pan.angle = 90
}
cleanup {
stop_motors()
servos.head_pan.angle = 90
}
}
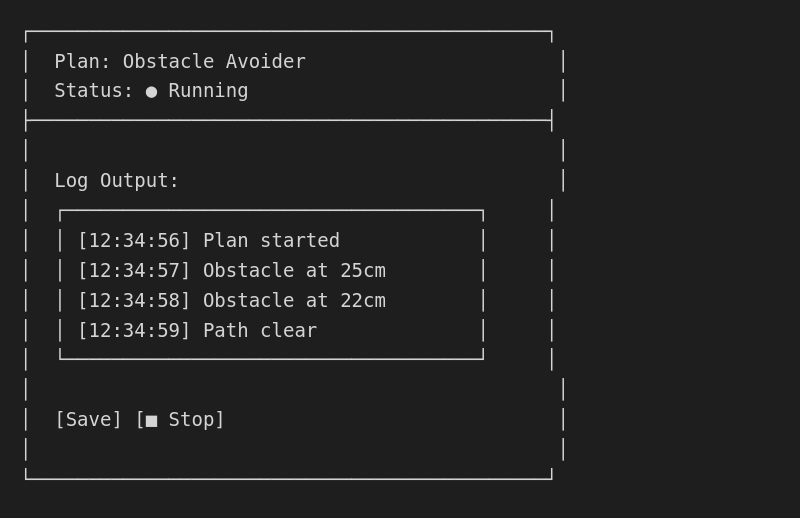
Step 4: Save and test
Save the plan
Click [Save] to store your Plan.
Run the plan
- Click [Run] to start execution
- Watch the Agent's behavior
- Click [Stop] to halt execution
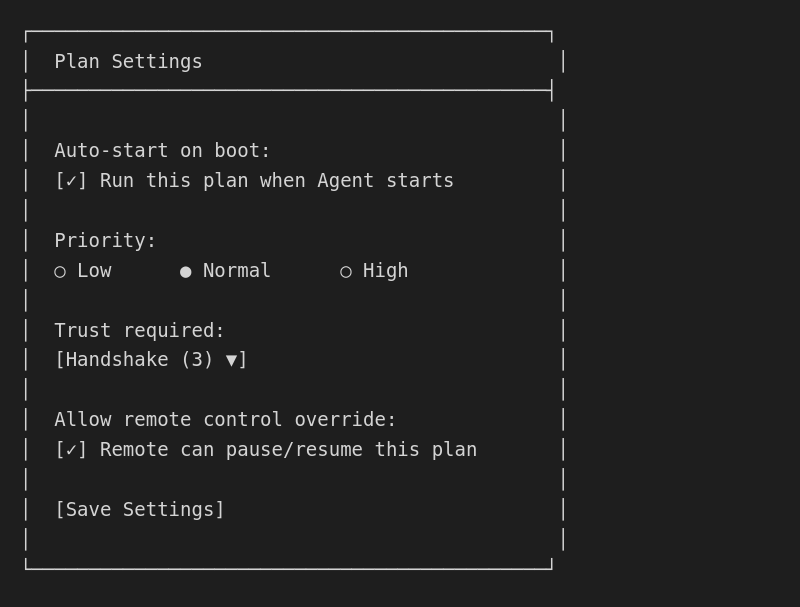
Plan settings
Configure how the Plan runs:
Available functions
Motor functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
drive(left, right) |
Set motor speeds (-100 to 100) |
stop_motors() |
Stop all motors |
turn_left(speed) |
Pivot turn left |
turn_right(speed) |
Pivot turn right |
Sensor functions
| Sensor | Properties |
|---|---|
sensors.distance.* |
front, left, right, back |
sensors.line.* |
left, center, right |
sensors.imu.* |
heading, pitch, roll |
sensors.battery.* |
level, voltage, charging |
Utility functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
delay(ms) |
Pause execution |
log(message) |
Write to log |
random(min, max) |
Random number |
abs(value) |
Absolute value |
Face functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
face.set_expression(name) |
happy, sad, surprised, neutral |
face.set_color(r, g, b) |
Set LED color |
Best practices
- Always include cleanup - Stop motors when plan ends
- Use delays in loops - Prevent CPU overload
- Add logging - Helps with debugging
- Test incrementally - Add features one at a time
- Handle edge cases - What if sensor fails?