Discovery and Pairing
How nodes find and trust each other
Discovery and Pairing
How OctoMY™ nodes find each other and establish trust relationships.
Did You Know?
The separation between discovery and pairing was inspired by Bluetooth's design, but taken further. In OctoMY™, discovering a node is purely technical - it just means "I can see you exist." The human decision of whether to trust that node is completely separate, and can be changed at any time without re-discovery.
Two separate processes
Discovery and pairing are intentionally separate:
| Process | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery | Automatic | Find nodes, exchange cryptographic identities |
| Pairing | Manual | User assigns trust levels to discovered nodes |
This separation means:
- Discovered nodes remain discovered regardless of trust status
- Users can trust/distrust/re-trust nodes freely
- Discovery records persist until explicitly removed
Discovery
Discovery is the automatic process of finding nodes and establishing secure identity verification.
Step 1: Establish physical proximity
Nodes prove physical proximity through one of these methods (in order of security):
| Method | Security | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NFC | Highest | Near-field requires touching devices |
| QR Code | High | Camera scan implies visual contact |
| Bluetooth | Medium | Short range implies nearby |
| Zoo/GPS | Low | GPS coordinates with expiring signatures |
| LAN | Lowest | Same network gateway |
Step 2: Exchange identities
Once proximity is established:
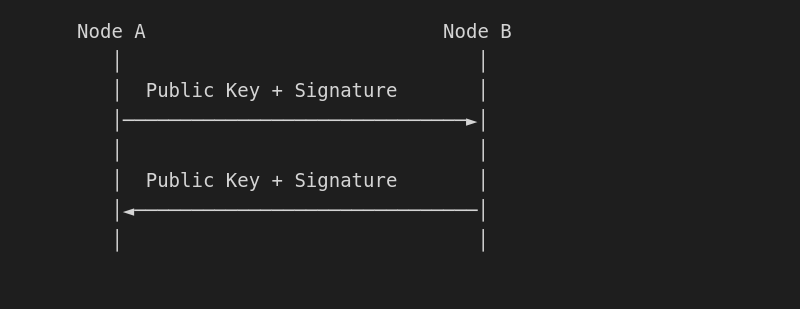
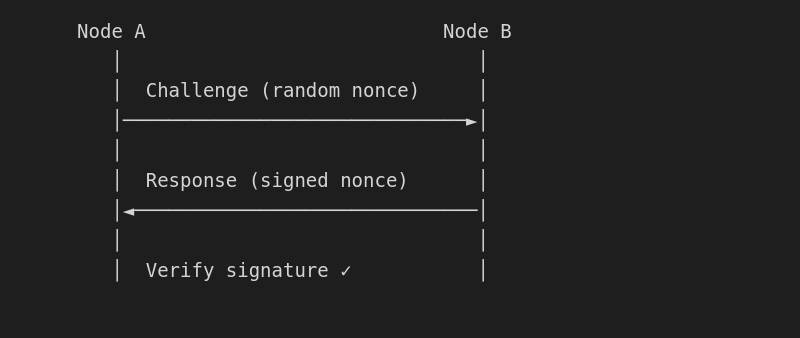
Step 3: Verify identities
Challenge/response proves each node controls its private key:
Step 4: Display identicons
Both nodes display their identicons (visual representations of cryptographic identity) for user verification.
![]()
Pairing
Pairing is the manual process where users assign trust to discovered nodes.
The user's role
After discovery, the user must:
- Verify identity - Compare identicons on both devices
- Assess trustworthiness - Is this the expected node?
- Assign trust level - Choose appropriate permissions
Trust assignment
Discovered Node: "Blue Spark"
Identicon: [████░██]
Select trust level:
○ Block - No communication
○ Ignore - Silently discard
○ Meet - Discovery only
○ Handshake - Can establish sessions
● Trust - Normal operation
○ Depend - Full trust
Trust properties
- Asymmetric - A trusting B doesn't mean B trusts A
- Per-node - Each relationship is independent
- Changeable - Trust can be adjusted anytime
- Logged - Changes create audit trail
Discovery methods in detail
NFC discovery
Strongest security guarantee through physical contact:
- Devices touch (NFC range ~4cm)
- Keys exchanged via NFC
- Full identity verification
- User confirms on both devices
QR code discovery
Camera-based discovery with visual confirmation:
- Node A displays QR code containing public key
- Node B scans with camera
- Node B sends its key via network
- Challenge/response verification
- Both users verify identicons
Bluetooth discovery
Proximity through radio range:
- Both nodes enable Bluetooth discovery
- Keys exchanged over Bluetooth
- Challenge/response verification
- Users verify identicons
Zoo discovery
For nodes not on the same network:
- Both nodes register with Zoo service
- GPS coordinates exchanged (with expiry)
- Zoo facilitates key exchange
- Users verify through separate channel
LAN discovery
For nodes on the same local network:
- UDP broadcast announces presence
- Nodes respond with public keys
- Challenge/response verification
- Users verify identicons
Security considerations
Why separate discovery and pairing?
- Discovery is technical - Proves cryptographic identity
- Pairing is human - User decides trust level
- Separation prevents automation - Trust requires human judgment
Multi-factor options
For additional security:
- SMS verification code
- Email confirmation
- Shared secret entry
- Physical token exchange
Removing discovery records
Removing discovery records is an advanced operation:
- Typically only needed for debugging
- Node will need to be re-discovered
- Useful if keys are compromised
Common scenarios
Pairing a new robot
- Start Agent on robot, Remote on phone
- Both on same WiFi → LAN discovery finds them
- Verify identicons match on both screens
- Set trust to "Trust" on both devices
- Robot and controller are paired
Adding a second controller
- New Remote discovers existing Agent
- Existing operator verifies new Remote's identity
- Agent operator grants trust to new Remote
- New Remote can now control Agent
Revoking access
- Open paired node in address book
- Change trust level to "Block"
- Node can no longer communicate
- Can be re-trusted later if needed