Sensors
Input devices and data sources
Sensors
Reference for OctoMY™ sensor types, configuration, and data handling.
Did You Know?
Sensor values in OctoMY™ include a "quality" indicator (0-100) that reflects signal reliability. This lets your Plans make smarter decisions - for example, you might trust a distance reading with quality 90+ but ignore one with quality below 50 when the ultrasonic sensor is getting interference.
Sensor overview
Sensors provide input data about the robot and its environment:
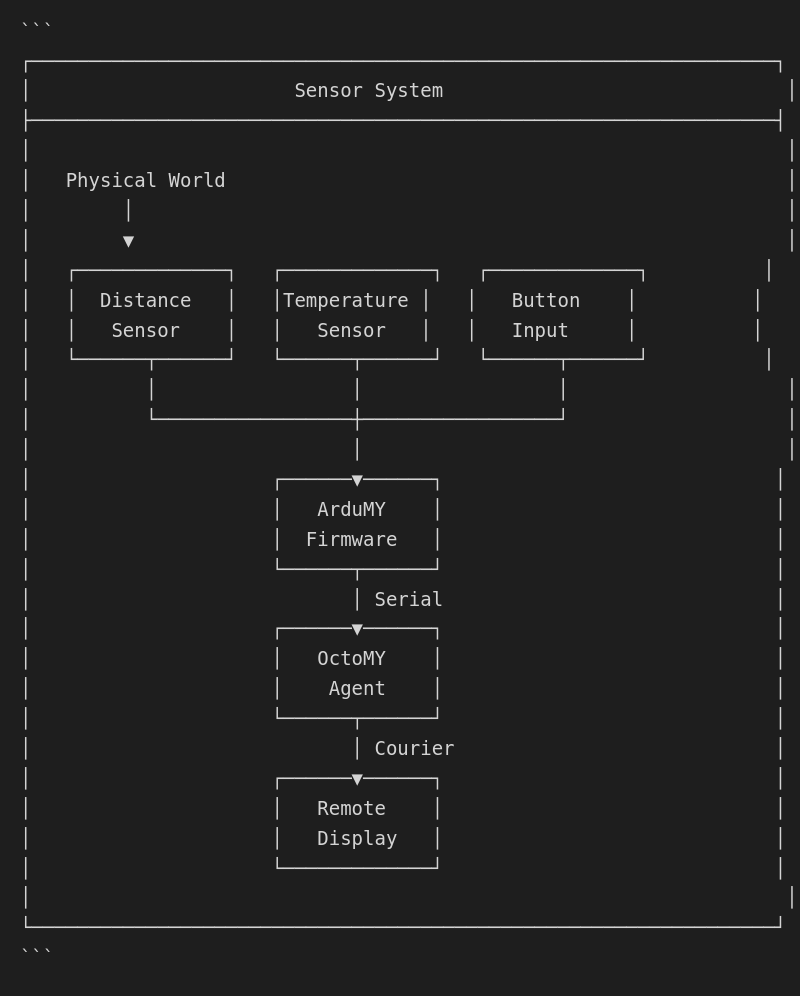
Sensor classification
From a usability perspective, sensors are classified in the following ways:
Signal quantization
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Analogue Value | A voltage corresponding to the sensor's value | Thermistor |
| Analogue PWM | Analogue timing of digital pulses | RC Servo position feedback |
| Digital | Discrete values sent as digital bits | GPS, I2C sensors |
Sample rate
How often is the sensor sampled? For encoders and tachometers, this could be very high (kHz). For a thermometer or GPS, it could be on the order of once per 5-second interval.
Sample acquisition
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Pull | The controller asks for a new value when needed | GPS |
| Event | The controller receives a value when available | Encoder or Tachometer |
| Push | The controller receives a steady stream of values | Thermometer |
Sensor types
Distance sensor
Ultrasonic or IR distance measurement:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 0 |
| Unit | Centimeters |
| Range | 2-400cm (typical) |
| Common Sensors | HC-SR04, Sharp IR |
struct DistanceSensorConfig {
quint8 triggerPin; // Trigger pin (ultrasonic)
quint8 echoPin; // Echo pin (ultrasonic)
quint8 analogPin; // Analog pin (IR)
quint16 minRange; // Minimum range (cm)
quint16 maxRange; // Maximum range (cm)
quint8 sampleCount; // Averaging samples
};
Angle/rotation sensor
Encoders and potentiometers:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 1 |
| Unit | Degrees (0.1 degree resolution) |
| Range | -32768 to 32767 (scaled) |
| Common Sensors | Rotary encoder, potentiometer |
struct AngleSensorConfig {
quint8 pinA; // Encoder pin A
quint8 pinB; // Encoder pin B
quint8 analogPin; // Analog input (potentiometer)
quint16 pulsesPerRev; // Pulses per revolution
bool invertDirection; // Reverse direction
};
Temperature sensor
Ambient and surface temperature:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 2 |
| Unit | Celsius (0.1 degree resolution) |
| Range | -40 to 125C (typical) |
| Common Sensors | DS18B20, TMP36, DHT22 |
struct TemperatureSensorConfig {
quint8 pin; // Data/analog pin
TemperatureType type; // DS18B20, TMP36, DHT, etc.
qint16 offset; // Calibration offset
quint8 resolution; // Bit resolution (9-12)
};
Voltage sensor
Battery and power monitoring:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 3 |
| Unit | Millivolts |
| Range | 0-65535mV |
| Common Uses | Battery monitor, power rail |
struct VoltageSensorConfig {
quint8 analogPin; // Analog input pin
float dividerRatio; // Voltage divider ratio
quint16 vRef; // Reference voltage (mV)
quint16 adcMax; // ADC maximum value
};
Current sensor
Motor and system current:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 4 |
| Unit | Milliamps |
| Range | 0-65535mA |
| Common Sensors | ACS712, INA219 |
struct CurrentSensorConfig {
quint8 pin; // Input pin
quint16 sensitivity; // mV per amp
quint16 offset; // Zero-current offset (mV)
bool bidirectional; // Can measure negative current
};
Light sensor
Ambient light measurement:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 5 |
| Unit | Lux (approximated) |
| Range | 0-65535 |
| Common Sensors | LDR, TSL2561 |
struct LightSensorConfig {
quint8 pin; // Analog/digital pin
LightSensorType type; // LDR, TSL2561, etc.
quint16 calibration; // Calibration factor
};
Acceleration sensor
3-axis accelerometer:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 6 |
| Unit | Milli-g (mg) |
| Range | -32768 to 32767 per axis |
| Common Sensors | MPU6050, ADXL345 |
struct AccelerationSensorConfig {
quint8 i2cAddress; // I2C address
AccelRange range; // 2g, 4g, 8g, 16g
quint8 sampleRate; // Samples per second
bool enableGyro; // Also enable gyroscope
};
Angular rate sensor
Gyroscope for rotation rate:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 7 |
| Unit | Milli-degrees per second |
| Range | -32768 to 32767 per axis |
| Common Sensors | MPU6050, L3GD20 |
struct GyroSensorConfig {
quint8 i2cAddress; // I2C address
GyroRange range; // 250, 500, 1000, 2000 dps
quint8 sampleRate; // Samples per second
};
Boolean sensor
Digital on/off inputs:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 8 |
| Unit | Boolean (0/1) |
| Range | True/False |
| Common Uses | Buttons, limit switches, bump sensors |
struct BooleanSensorConfig {
quint8 pin; // Digital input pin
bool pullup; // Enable internal pullup
bool invertLogic; // Invert true/false
quint16 debounceMs; // Debounce time (ms)
};
Sensor message format
SensorsMessage structure
struct SensorsMessage {
quint64 timestamp; // Message timestamp (ms)
quint8 sensorCount; // Number of readings
SensorReading readings[]; // Variable-length array
};
struct SensorReading {
quint8 sensorId; // Sensor identifier
quint8 type; // SensorType enum
quint16 value; // Scaled sensor value
quint8 quality; // Signal quality (0-100)
};
Value scaling
Sensor values are scaled to fit in 16 bits:
| Sensor Type | Raw Range | Scaled | Scale Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distance | 0-400cm | 0-4000 | 10x |
| Angle | -180 to 180 | -1800 to 1800 | 10x |
| Temperature | -40 to 125C | -400 to 1250 | 10x |
| Voltage | 0-15000mV | 0-15000 | 1x |
| Current | 0-10000mA | 0-10000 | 1x |
| Light | 0-65535 | 0-65535 | 1x |
| Acceleration | -16g to 16g | -16000 to 16000 | 1000x |
Reading sensors
From OPAL plans
// Read individual sensors
var distance = sensors.distance.front
var temperature = sensors.temperature.ambient
var battery = sensors.voltage.battery
// Check boolean sensors
if sensors.bump.front {
stop()
}
// Read multiple sensors
var readings = sensors.all()
for reading in readings {
log("Sensor " + reading.id + ": " + reading.value)
}
From C++
// Get sensor data via courier
connect(sensorsCourier, &SensorsCourier::sensorsReceived,
[](const SensorsMessage& msg) {
for (int i = 0; i < msg.sensorCount; i++) {
auto& reading = msg.readings[i];
processSensorReading(reading);
}
});
// Access cached values
float distance = sensorManager->value("distance.front");
bool bumped = sensorManager->boolValue("bump.front");
Sensor configuration
Configuration file format
{
"sensors": [
{
"id": 0,
"type": "DISTANCE",
"name": "front",
"config": {
"triggerPin": 7,
"echoPin": 8,
"maxRange": 400
}
},
{
"id": 1,
"type": "DISTANCE",
"name": "left",
"config": {
"triggerPin": 9,
"echoPin": 10,
"maxRange": 400
}
},
{
"id": 2,
"type": "BOOLEAN",
"name": "bump.front",
"config": {
"pin": 2,
"pullup": true,
"invertLogic": true,
"debounceMs": 50
}
},
{
"id": 3,
"type": "VOLTAGE",
"name": "battery",
"config": {
"analogPin": 0,
"dividerRatio": 4.0,
"vRef": 5000
}
}
]
}
Sensor naming convention
Sensors use hierarchical names:
{category}.{location}
Examples:
- distance.front
- distance.left
- distance.right
- bump.front
- bump.left
- bump.right
- temperature.ambient
- temperature.motor
- voltage.battery
- current.motor.left
Sensor filtering
Moving average
struct FilterConfig {
quint8 windowSize; // Number of samples
bool medianFilter; // Use median instead of mean
};
// In OPAL
var smoothed = smooth(sensors.distance.front, 10)
Low-pass filter
struct LowPassConfig {
float alpha; // Filter coefficient (0-1)
// Higher alpha = more responsive, more noise
// Lower alpha = smoother, more lag
};
Kalman filter
For sensor fusion:
class KalmanFilter {
public:
void setProcessNoise(float q);
void setMeasurementNoise(float r);
float update(float measurement);
};
Sensor quality
Quality indicators
| Quality | Value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent | 90-100 | Strong, reliable signal |
| Good | 70-89 | Normal operation |
| Fair | 50-69 | Degraded but usable |
| Poor | 25-49 | Unreliable |
| Bad | 0-24 | No valid data |
Quality factors
- Signal strength
- Noise level
- Out-of-range conditions
- Sensor error flags
- Age of reading
Sensor events
Threshold events
// Trigger when sensor crosses threshold
trigger on sensors.distance.front < 30 {
stop()
}
// Trigger on change
trigger on change(sensors.bump.front) {
if sensors.bump.front {
backup()
}
}
Sensor callbacks
// C++ sensor callbacks
sensorManager->onThreshold("distance.front", 30, BELOW,
[]() {
qDebug() << "Obstacle detected!";
});
sensorManager->onChange("bump.front",
[](bool value) {
qDebug() << "Bump sensor:" << value;
});
Sensor widgets
RealtimeValuesWidget
Display live sensor values:
class RealtimeValuesWidget : public QWidget {
public:
void setSensorSet(SensorSet* sensors);
void setUpdateRate(int ms);
void showSensor(const QString& name, bool visible);
};
SensorGraphWidget
Plot sensor values over time:
class SensorGraphWidget : public QWidget {
public:
void addSensor(const QString& name, const QColor& color);
void setTimeWindow(int seconds);
void setYRange(float min, float max);
};
Common sensor configurations
Basic robot
{
"sensors": [
{"id": 0, "type": "DISTANCE", "name": "front"},
{"id": 1, "type": "BOOLEAN", "name": "bump.front"},
{"id": 2, "type": "BOOLEAN", "name": "bump.left"},
{"id": 3, "type": "BOOLEAN", "name": "bump.right"},
{"id": 4, "type": "VOLTAGE", "name": "battery"}
]
}
Line-following robot
{
"sensors": [
{"id": 0, "type": "BOOLEAN", "name": "line.left"},
{"id": 1, "type": "BOOLEAN", "name": "line.center"},
{"id": 2, "type": "BOOLEAN", "name": "line.right"},
{"id": 3, "type": "DISTANCE", "name": "front"}
]
}
Autonomous robot
{
"sensors": [
{"id": 0, "type": "DISTANCE", "name": "front"},
{"id": 1, "type": "DISTANCE", "name": "left"},
{"id": 2, "type": "DISTANCE", "name": "right"},
{"id": 3, "type": "ACCELERATION", "name": "imu"},
{"id": 4, "type": "ANGULAR_RATE", "name": "gyro"},
{"id": 5, "type": "ANGLE", "name": "wheel.left"},
{"id": 6, "type": "ANGLE", "name": "wheel.right"},
{"id": 7, "type": "VOLTAGE", "name": "battery"},
{"id": 8, "type": "CURRENT", "name": "motor"}
]
}
Troubleshooting
Common issues
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Noisy readings | Electrical interference | Add filtering, shielding |
| Wrong values | Calibration | Verify scale factors |
| No readings | Pin configuration | Check wiring and pins |
| Intermittent | Loose connection | Check connectors |
| Slow response | Low sample rate | Increase update rate |
Debugging sensors
// Enable sensor debugging
QLoggingCategory::setFilterRules("octomy.sensors.debug=true");
// Log all readings
sensorManager->setLogging(true);
// Check sensor status
for (auto& sensor : sensorManager->allSensors()) {
qDebug() << sensor.name
<< "value:" << sensor.lastValue
<< "quality:" << sensor.quality
<< "age:" << sensor.lastUpdateMs << "ms";
}