Lobes
Locomotion controllers and kinematics
Lobes
Reference for OctoMY™ Lobes - pluggable locomotion controllers that translate high-level commands into actuator control.
Did You Know?
Lobes are named after brain regions because they encapsulate decision-making that can run either on the OctoMY™ Agent or directly on the controller hardware. When running on-board the Arduino, lobes provide lower latency, reduced power draw, and resilience - your robot can keep walking even if it briefly loses connection to the Agent.
What is a Lobe?
Lobes are named after the distinct regions in our brain dedicated to specific tasks. In OctoMY™, Lobes represent real-time processing units that take input from sensors and user controls and generate output to actuators.
A Lobe encapsulates decision-making into a unit that can run in different environments:
- If your controller doesn't support Lobes, the processing runs in software on the OctoMY™ Agent
- If the controller supports Lobes, processing moves on-board the controller itself
Benefits of on-board processing
When Lobes run on the controller hardware:
- The Agent is freed up to focus on other tasks
- Less error-prone operation as signals don't travel as far
- Lower power draw
- More responsive operation
- More resilient operation (works even if Agent connection is lost)
Since Lobes are well-defined, they can be tested in simulation environments before deployment to real hardware.
Example: car steering lobe
Basic version
A simple car steering lobe:
- Input: Throttle position (from remote control)
- Input: Steering angle (from remote control)
- Output: Motor throttle (brushless motor ESC)
- Output: Steering servo (RC servo)
In this basic example, the Lobe simply passes throttle input to the motor and steering angle to the steering servo. The key is that it sets up expectations - this is made to control any car-like robot, allowing a fancy UI with steering wheel and foot pedal to be created.
Advanced version with sensors
Adding IMU and GPS enables advanced processing:
- Input: Throttle position (from remote control)
- Input: Steering angle (from remote control)
- Input: IMU (inertial measurement unit)
- Input: GPS (global positioning system)
- Output: Motor throttle (brushless motor ESC)
- Output: Steering servo (RC servo)
Now the Lobe can perform:
- Traction control - Burst throttle if vehicle movement doesn't match wheel speed
- Adaptive throttle sensitivity - Less throttle at lower speeds
- Adaptive steering sensitivity - Less steering angle at higher speeds
- Adaptive steering correction - Rapid adjustments based on vehicle direction vs travel direction to avoid spinning out
- Drift mode - Detect slip and adjust steering to favor a drifting angle
This takes a basic toy to a full race-car with just firmware changes.
Lobe overview
Lobes provide abstraction between movement intent and actuator control:
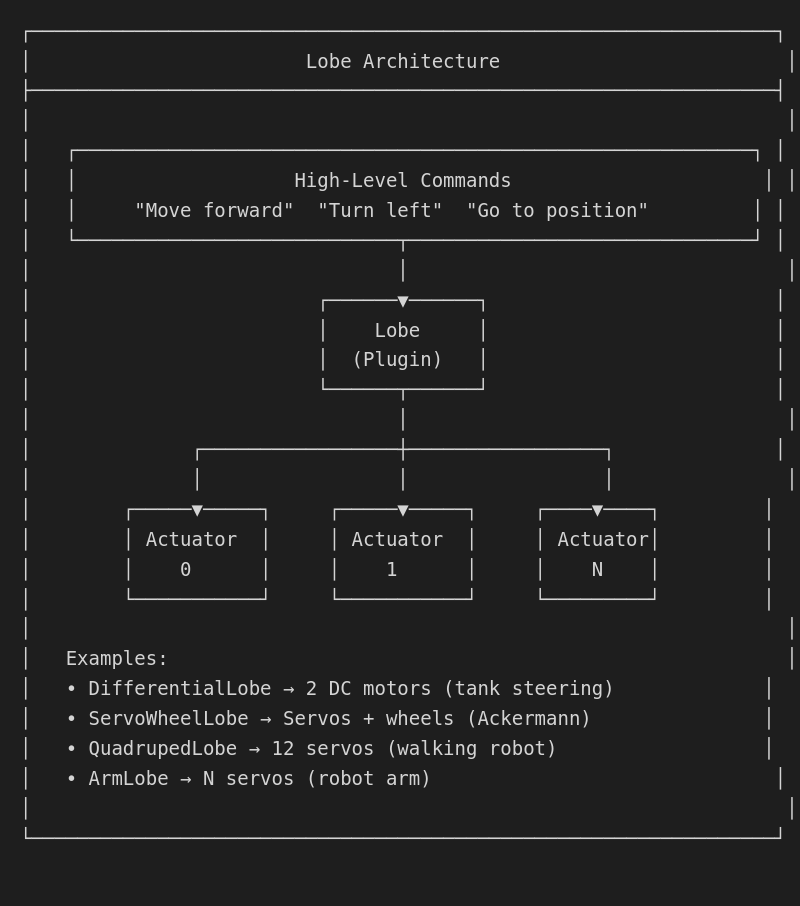
Lobe types
DifferentialLobe
Two-wheel differential drive (tank steering):
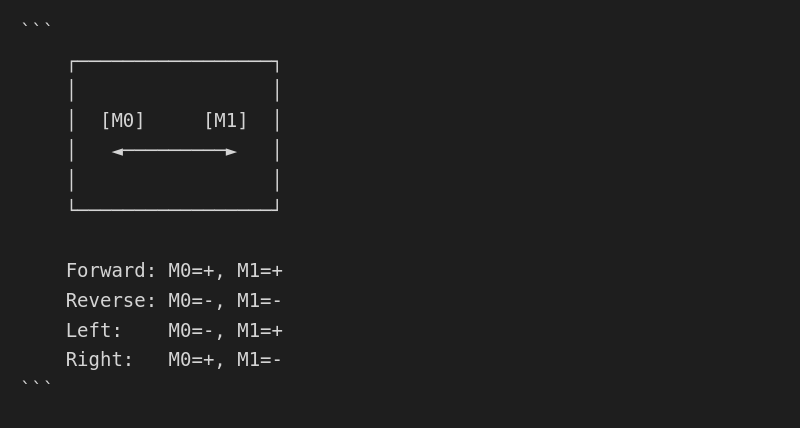
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | DIFFERENTIAL |
| Actuators | 2 DC motors |
| Input | (speed, turn) or (left, right) |
class DifferentialLobe : public Lobe {
public:
// Movement commands
void drive(float speed, float turn); // -1 to 1
void tank(float left, float right); // -1 to 1
void stop();
// Configuration
void setWheelBase(float mm);
void setWheelDiameter(float mm);
void setMaxSpeed(float mmPerSec);
};
AckermannLobe
Car-like steering with front wheel steering:
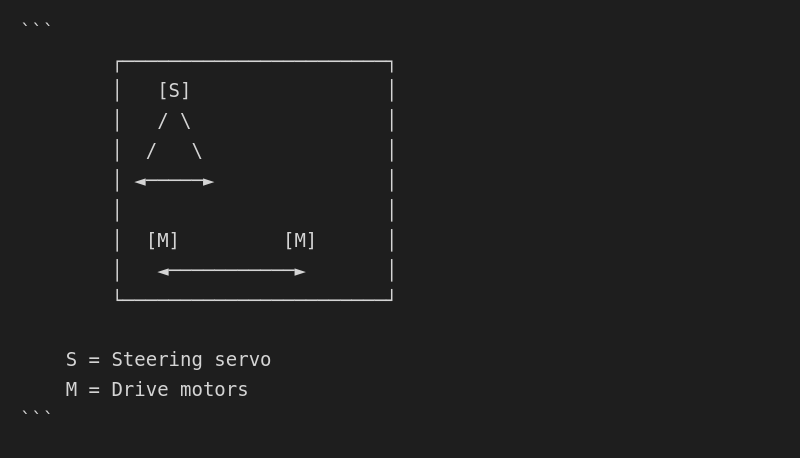
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | ACKERMANN |
| Actuators | 1-2 DC motors + 1 steering servo |
| Input | (speed, steering_angle) |
class AckermannLobe : public Lobe {
public:
void drive(float speed, float steeringAngle);
void setMaxSteeringAngle(float degrees);
void setWheelbase(float mm);
void setTrackWidth(float mm);
};
MecanumLobe
Four mecanum wheels for omnidirectional movement:
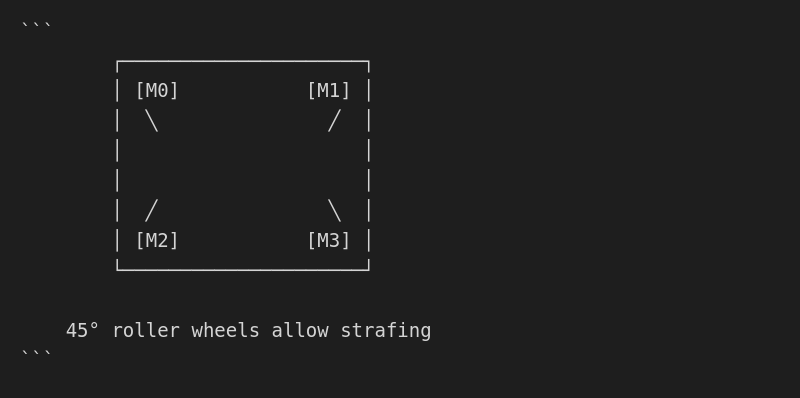
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | MECANUM |
| Actuators | 4 DC motors |
| Input | (x, y, rotation) |
class MecanumLobe : public Lobe {
public:
void move(float x, float y, float rotation); // -1 to 1
void strafe(float angle, float speed);
void rotate(float speed);
};
QuadrupedLobe
Four-legged walking robot:

| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | QUADRUPED |
| Actuators | 8-12 servos |
| Input | (direction, speed) or gait commands |
class QuadrupedLobe : public Lobe {
public:
// Movement
void walk(float direction, float speed);
void turn(float rate);
void strafe(float angle, float speed);
// Gaits
void setGait(GaitType gait); // WALK, TROT, CRAWL
void setStepHeight(float mm);
void setStepLength(float mm);
// Pose
void setBodyHeight(float mm);
void setBodyPitch(float degrees);
void setBodyRoll(float degrees);
};
enum GaitType {
GAIT_WALK, // 3 legs on ground
GAIT_TROT, // Diagonal pairs
GAIT_CRAWL, // 1 leg at a time
GAIT_BOUND, // Front/back pairs
};
HexapodLobe
Six-legged walking robot:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | HEXAPOD |
| Actuators | 12-18 servos |
| Input | Similar to quadruped |
class HexapodLobe : public QuadrupedLobe {
// Inherits quadruped interface
// Additional tripod gait support
};
ArmLobe
Robotic arm with inverse kinematics:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | ARM |
| Actuators | 3-6+ servos |
| Input | Joint angles or cartesian (x, y, z) |
class ArmLobe : public Lobe {
public:
// Joint control
void setJoint(int joint, float angle);
void setAllJoints(const QVector<float>& angles);
// Cartesian control (with IK)
void moveTo(float x, float y, float z);
void moveRelative(float dx, float dy, float dz);
// Gripper
void grip(float amount); // 0=open, 1=closed
void open();
void close();
// Kinematics
void setLinkLengths(const QVector<float>& lengths);
QVector3D currentPosition() const;
};
Lobe interface
Base class
class Lobe : public QObject {
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit Lobe(QObject* parent = nullptr);
virtual ~Lobe();
// Identification
virtual QString name() const = 0;
virtual LobeType type() const = 0;
// Lifecycle
virtual void activate();
virtual void deactivate();
bool isActive() const;
// Actuator binding
void setActuatorSet(ArduMYActuatorSet* actuators);
void bindActuator(int slot, int actuatorId);
// Update loop
virtual void update(quint64 deltaMs);
// Emergency
virtual void emergencyStop();
signals:
void activated();
void deactivated();
void error(const QString& message);
protected:
virtual void setActuatorValue(int slot, float value);
float getActuatorValue(int slot) const;
};
Lobe types enum
enum LobeType {
LOBE_DIFFERENTIAL, // Tank drive
LOBE_ACKERMANN, // Car steering
LOBE_MECANUM, // Omnidirectional wheels
LOBE_QUADRUPED, // 4-leg walking
LOBE_HEXAPOD, // 6-leg walking
LOBE_ARM, // Robot arm
LOBE_CUSTOM, // User-defined
};
Lobe configuration
Configuration file
{
"lobe": {
"type": "DIFFERENTIAL",
"name": "MainDrive",
"config": {
"wheelBase": 150,
"wheelDiameter": 65,
"maxSpeed": 500,
"invertLeft": false,
"invertRight": true
},
"actuators": {
"left": 0,
"right": 1
}
}
}
Quadruped configuration
{
"lobe": {
"type": "QUADRUPED",
"name": "WalkingLobe",
"config": {
"legLength": [50, 70, 80],
"bodyWidth": 100,
"bodyLength": 150,
"defaultHeight": 60,
"defaultGait": "TROT"
},
"actuators": {
"leg0_hip": 0,
"leg0_knee": 1,
"leg0_ankle": 2,
"leg1_hip": 3,
"leg1_knee": 4,
"leg1_ankle": 5,
"leg2_hip": 6,
"leg2_knee": 7,
"leg2_ankle": 8,
"leg3_hip": 9,
"leg3_knee": 10,
"leg3_ankle": 11
}
}
}
Using lobes
From OPAL plans
// Differential drive
lobe.drive(0.5, 0.0) // Forward at half speed
lobe.drive(0.5, 0.3) // Forward with right turn
lobe.tank(0.5, -0.5) // Spin in place
lobe.stop()
// Quadruped
lobe.walk(0, 0.5) // Walk forward
lobe.setGait("TROT") // Change gait
lobe.strafe(90, 0.3) // Strafe right
// Arm
lobe.moveTo(100, 50, 80) // Move to position
lobe.grip(1.0) // Close gripper
From C++
// Create and configure lobe
auto lobe = new DifferentialLobe(this);
lobe->setActuatorSet(actuatorSet);
lobe->bindActuator(0, 0); // Left motor
lobe->bindActuator(1, 1); // Right motor
lobe->setWheelBase(150);
lobe->activate();
// Control
lobe->drive(0.5, 0.0); // Forward
// Update loop
void onTimer() {
lobe->update(16); // 60fps
}
Kinematics
Differential drive kinematics
// Forward kinematics: wheel speeds → robot velocity
struct DifferentialKinematics {
float wheelBase; // Distance between wheels
// Convert wheel speeds to robot velocity
void forwardKinematics(float vLeft, float vRight,
float& vLinear, float& vAngular) {
vLinear = (vRight + vLeft) / 2.0f;
vAngular = (vRight - vLeft) / wheelBase;
}
// Convert robot velocity to wheel speeds
void inverseKinematics(float vLinear, float vAngular,
float& vLeft, float& vRight) {
vLeft = vLinear - (vAngular * wheelBase / 2.0f);
vRight = vLinear + (vAngular * wheelBase / 2.0f);
}
};
Mecanum kinematics
// Mecanum inverse kinematics
void mecanumIK(float vx, float vy, float omega,
float& m0, float& m1, float& m2, float& m3) {
// Front-left, front-right, back-left, back-right
m0 = vx - vy - omega;
m1 = vx + vy + omega;
m2 = vx + vy - omega;
m3 = vx - vy + omega;
// Normalize if any exceeds 1.0
float maxVal = qMax(qMax(qAbs(m0), qAbs(m1)),
qMax(qAbs(m2), qAbs(m3)));
if (maxVal > 1.0f) {
m0 /= maxVal;
m1 /= maxVal;
m2 /= maxVal;
m3 /= maxVal;
}
}
Arm inverse kinematics
// Simple 2-link arm IK
bool arm2LinkIK(float x, float y, float L1, float L2,
float& theta1, float& theta2) {
float d = qSqrt(x*x + y*y);
if (d > L1 + L2) return false; // Out of reach
float cos_theta2 = (x*x + y*y - L1*L1 - L2*L2) /
(2 * L1 * L2);
theta2 = qAcos(cos_theta2);
float k1 = L1 + L2 * qCos(theta2);
float k2 = L2 * qSin(theta2);
theta1 = qAtan2(y, x) - qAtan2(k2, k1);
return true;
}
Custom lobes
Creating a custom lobe
class MyCustomLobe : public Lobe {
Q_OBJECT
public:
MyCustomLobe(QObject* parent = nullptr)
: Lobe(parent) {}
QString name() const override {
return "MyCustomLobe";
}
LobeType type() const override {
return LOBE_CUSTOM;
}
void update(quint64 deltaMs) override {
// Update actuators based on current commands
// Called every frame
}
void emergencyStop() override {
// Stop all movement immediately
for (int i = 0; i < actuatorCount(); i++) {
setActuatorValue(i, 0);
}
}
// Custom methods
void myCustomMovement(float param1, float param2) {
// Implement custom kinematics
}
};
Registering custom lobe
// Register lobe factory
LobeManager::registerType("MY_CUSTOM",
[](QObject* parent) {
return new MyCustomLobe(parent);
});
// Create from configuration
auto lobe = LobeManager::create("MY_CUSTOM", config);
Lobe manager
LobeManager class
class LobeManager : public QObject {
public:
// Lobe management
void setLobe(Lobe* lobe);
Lobe* lobe() const;
// Factory
static Lobe* create(const QString& type,
const QJsonObject& config,
QObject* parent);
// Registration
static void registerType(const QString& type,
LobeFactory factory);
signals:
void lobeChanged(Lobe* lobe);
void lobeError(const QString& error);
};
Troubleshooting
Common issues
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Robot goes wrong direction | Motor wiring | Set invert flags |
| Robot curves when going straight | Motor speed difference | Calibrate motors |
| Arm can't reach position | Out of workspace | Check IK limits |
| Walking robot falls | Wrong gait timing | Tune step timing |
| Jerky movement | Update rate too low | Increase update frequency |
Debugging lobes
// Enable lobe debugging
QLoggingCategory::setFilterRules("octomy.lobe.debug=true");
// Log actuator commands
lobe->setDebugLogging(true);
// Check lobe state
qDebug() << "Lobe:" << lobe->name()
<< "Active:" << lobe->isActive()
<< "Actuators:" << lobe->actuatorCount();