Actuators
Motors, servos, and output devices
Actuators
Reference for OctoMY™ actuator types, configuration, and control.
Pro Tip
Always configure the motor safety timeout (
setSafetyTimeout(500)) for your actuators. If the Agent loses connection to the Remote, motors will automatically stop after the timeout period instead of continuing at the last commanded speed - this prevents runaways and protects both the robot and its surroundings.
Actuator overview
Actuators are output devices that convert commands into physical action:
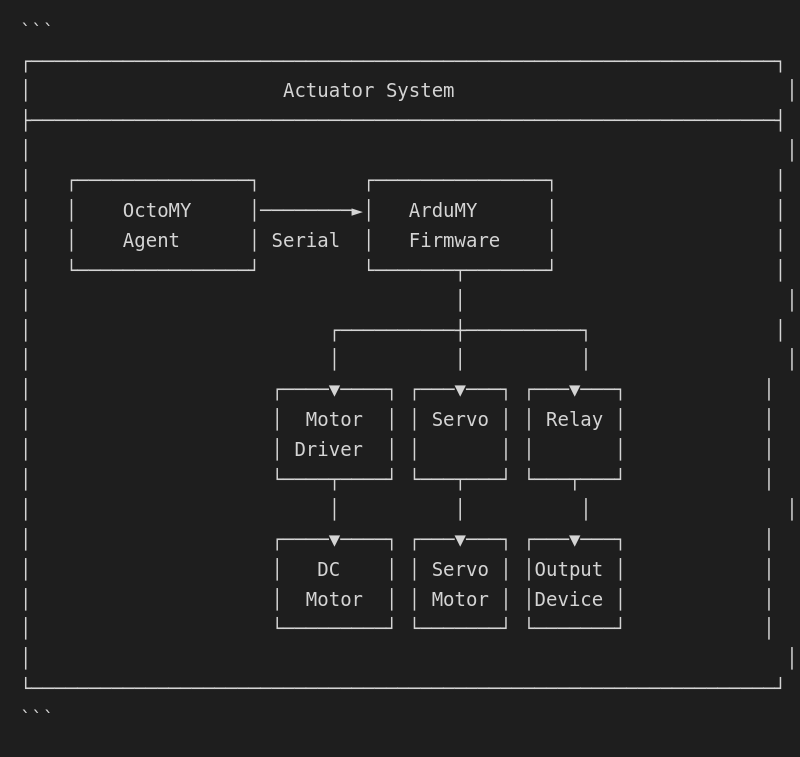
Actuator classification
From a usability perspective, actuators are classified in the following ways:
Motion type
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Rotary | Actuators that produce rotational motion | DC motors, servo motors, stepper motors |
| Linear | Actuators that produce linear motion (straight line) | Linear actuators, solenoids, lead screw actuators |
Movement range
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous | Capable of continuous 360-degree or infinite motion | DC motors, stepper motors |
| Ranged | Limited to a specific range of motion (e.g., 0 to 180 degrees) | Servo motors, piezoelectric actuators |
Feedback type
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Position Feedback | Provides feedback on the position of the actuator | Servo motors with potentiometers |
| Speed Feedback | Provides feedback on the speed of movement | Rotary encoders, tachometers |
| Force Feedback | Provides feedback on the force or load applied | Actuators with built-in load cells |
Control method
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Open-loop | Operates without feedback; performs predefined actions | Basic DC motors, solenoids |
| Closed-loop | Uses feedback mechanisms to adjust and control accurately | Servo motors, stepper motors with feedback |
Power source
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Electric | Actuators powered by electrical energy | DC motors, AC motors, stepper motors |
| Pneumatic | Actuators that use compressed air to generate motion | Pneumatic cylinders, pneumatic valves |
| Hydraulic | Actuators that use fluid pressure for movement | Hydraulic rams, hydraulic motors |
Actuation mechanism
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic | Uses magnetic fields for motion generation | DC motors, stepper motors |
| Piezoelectric | Uses electrical charge in piezoelectric materials | Precise positioning devices |
| Electrostatic | Uses electrostatic force, typically in micro-scale devices | MEMS actuators, electrostatic relays |
Actuator types
DC Motor
Standard brushed DC motors with PWM speed control:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 0 |
| Control | PWM (0-255) or signed (-100 to 100) |
| Direction | Forward/Reverse |
| Common Uses | Wheels, tracks, propellers |
struct DCMotorConfig {
quint8 pwmPin; // PWM output pin
quint8 directionPin; // Direction control pin (optional)
quint8 enablePin; // Enable pin (optional)
bool invertDirection; // Reverse direction polarity
quint16 maxPWM; // Maximum PWM value (default 255)
};
Servo motor
Standard hobby servos with angular position control:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 1 |
| Control | Angle (0-180 degrees) |
| Range | Configurable min/max angle |
| Common Uses | Steering, arms, pan/tilt |
struct ServoConfig {
quint8 pin; // Servo signal pin
quint16 minPulse; // Minimum pulse width (us)
quint16 maxPulse; // Maximum pulse width (us)
quint8 minAngle; // Minimum angle (degrees)
quint8 maxAngle; // Maximum angle (degrees)
quint8 defaultAngle; // Default/home position
};
Continuous servo
Servos modified for continuous rotation:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 2 |
| Control | Speed (-100 to 100) |
| Direction | Forward/Reverse |
| Common Uses | Wheels, rotating platforms |
struct ContinuousServoConfig {
quint8 pin; // Servo signal pin
quint16 stopPulse; // Pulse width for stop (typically 1500)
quint16 minPulse; // Minimum pulse (full reverse)
quint16 maxPulse; // Maximum pulse (full forward)
};
Stepper motor
Stepper motors with position and speed control:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 3 |
| Control | Steps or degrees |
| Modes | Full step, half step, microstepping |
| Common Uses | Precise positioning, CNC |
struct StepperConfig {
quint8 stepPin; // Step pulse pin
quint8 dirPin; // Direction pin
quint8 enablePin; // Enable pin (optional)
quint16 stepsPerRev; // Steps per revolution
quint8 microstepping; // Microstepping mode (1, 2, 4, 8, 16)
quint16 maxSpeed; // Maximum speed (steps/sec)
quint16 acceleration; // Acceleration (steps/sec^2)
};
Relay
On/off switching for high-power devices:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 4 |
| Control | On (1) / Off (0) |
| Common Uses | Lights, pumps, heaters |
struct RelayConfig {
quint8 pin; // Control pin
bool activeHigh; // True if HIGH = ON
bool defaultState; // Default state on startup
};
PWM output
Raw PWM signal for custom applications:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Type ID | 5 |
| Control | Duty cycle (0-255) |
| Common Uses | LEDs, fans, custom control |
struct PWMConfig {
quint8 pin; // PWM output pin
quint16 frequency; // PWM frequency (Hz)
quint8 defaultValue; // Default duty cycle
};
Actuator configuration
ArduMYActuator structure
struct ArduMYActuator {
quint8 id; // Unique actuator ID
ActuatorType type; // Type enum
QString name; // Human-readable name
quint8 flags; // Enable bits and options
ActuatorConfig config; // Type-specific config
ActuatorState state; // Current state
};
Enable flags
enum ActuatorFlags {
ACTUATOR_ENABLED = 0x01, // Actuator is enabled
ACTUATOR_INVERTED = 0x02, // Invert direction/value
ACTUATOR_HOMED = 0x04, // Has been homed
ACTUATOR_MOVING = 0x08, // Currently in motion
ACTUATOR_ERROR = 0x10, // Error condition
};
Actuator sets
ArduMYActuatorSet
Collection of actuators managed together:
class ArduMYActuatorSet {
public:
// Actuator management
void addActuator(const ArduMYActuator& actuator);
void removeActuator(quint8 id);
ArduMYActuator* actuator(quint8 id);
// Bulk operations
void enableAll();
void disableAll();
void homeAll();
// Serialization
QByteArray serialize() const;
bool deserialize(const QByteArray& data);
// Iteration
int count() const;
ArduMYActuator& operator[](int index);
};
Configuration file format
Actuator sets can be saved/loaded from JSON:
{
"actuators": [
{
"id": 0,
"type": "DC_MOTOR",
"name": "Left Motor",
"config": {
"pwmPin": 3,
"directionPin": 4,
"invertDirection": false
}
},
{
"id": 1,
"type": "DC_MOTOR",
"name": "Right Motor",
"config": {
"pwmPin": 5,
"directionPin": 6,
"invertDirection": true
}
},
{
"id": 2,
"type": "SERVO",
"name": "Pan Servo",
"config": {
"pin": 9,
"minAngle": 0,
"maxAngle": 180,
"defaultAngle": 90
}
}
]
}
Actuator commands
Command structure
struct ActuatorCommand {
quint8 actuatorId; // Target actuator
quint8 type; // Command type
qint16 value; // Target value
quint8 flags; // Command flags
};
Command types
| Type | Description | Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| SET_VALUE | Set actuator value | Type-dependent |
| SET_SPEED | Set movement speed | 0-100% |
| HOME | Move to home position | N/A |
| STOP | Immediate stop | N/A |
| ENABLE | Enable actuator | 0/1 |
| DISABLE | Disable actuator | N/A |
Sending commands
// From OPAL Plan
actuators.set(0, 75); // Motor 0 to 75%
actuators.set(1, -50); // Motor 1 to -50% (reverse)
actuators.set(2, 90); // Servo to 90 degrees
// Multiple commands
actuators.setAll([75, 75, 90, 45]);
// Stop all
actuators.stopAll();
Value representations
ArduMYActuatorValue
Actuators use a union type for values:
union ActuatorValue {
qint8 byte; // 8-bit signed
quint8 ubyte; // 8-bit unsigned
qint16 word; // 16-bit signed
quint16 uword; // 16-bit unsigned
qint32 dword; // 32-bit signed
quint32 udword; // 32-bit unsigned
float real; // 32-bit float
};
Value types by actuator
| Actuator Type | Value Type | Range | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC Motor | byte | -100 to 100 | % speed |
| Servo | uword | 0 to 180 | degrees |
| Continuous Servo | byte | -100 to 100 | % speed |
| Stepper | dword | varies | steps |
| Relay | ubyte | 0 or 1 | on/off |
| PWM | ubyte | 0 to 255 | duty |
Safety features
Motor safety timeout
Motors automatically stop if no command received:
struct SafetyConfig {
quint16 timeoutMs; // Timeout in milliseconds
bool emergencyStop; // Stop immediately on timeout
bool coastStop; // Coast to stop vs brake
};
// Configuration
actuators.setSafetyTimeout(500); // 500ms timeout
actuators.setEmergencyStop(true);
Current limiting
struct CurrentLimit {
quint16 maxCurrent; // Maximum current (mA)
quint16 warnCurrent; // Warning threshold (mA)
bool autoLimit; // Auto-reduce on overcurrent
};
Position limits
For servos and steppers:
struct PositionLimits {
qint32 minPosition; // Minimum position
qint32 maxPosition; // Maximum position
bool softLimits; // Enable software limits
bool hardLimits; // Enable hardware limit switches
};
Actuator widgets
ActuatorWidget
UI component for individual actuator control:
class ActuatorWidget : public QWidget {
public:
void setActuator(ArduMYActuator* actuator);
void setValue(qint16 value);
qint16 value() const;
signals:
void valueChanged(qint16 value);
void enabled(bool state);
};
ActuatorSetWidget
UI for managing multiple actuators:
class ActuatorSetWidget : public QWidget {
public:
void setActuatorSet(ArduMYActuatorSet* set);
void refresh();
public slots:
void enableAll();
void disableAll();
void homeAll();
void stopAll();
};
Common configurations
Differential drive robot
Two-wheel robot with tank steering:
{
"actuators": [
{"id": 0, "type": "DC_MOTOR", "name": "Left", "config": {"pwmPin": 3, "directionPin": 4}},
{"id": 1, "type": "DC_MOTOR", "name": "Right", "config": {"pwmPin": 5, "directionPin": 6}}
]
}
Pan-tilt camera
Two-axis camera mount:
{
"actuators": [
{"id": 0, "type": "SERVO", "name": "Pan", "config": {"pin": 9, "minAngle": 0, "maxAngle": 180}},
{"id": 1, "type": "SERVO", "name": "Tilt", "config": {"pin": 10, "minAngle": 30, "maxAngle": 150}}
]
}
Robot arm
Multi-joint arm with gripper:
{
"actuators": [
{"id": 0, "type": "SERVO", "name": "Base", "config": {"pin": 3}},
{"id": 1, "type": "SERVO", "name": "Shoulder", "config": {"pin": 5}},
{"id": 2, "type": "SERVO", "name": "Elbow", "config": {"pin": 6}},
{"id": 3, "type": "SERVO", "name": "Wrist", "config": {"pin": 9}},
{"id": 4, "type": "SERVO", "name": "Gripper", "config": {"pin": 10}}
]
}
Troubleshooting
Common issues
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Motor doesn't move | Wrong pin | Verify pin configuration |
| Motor runs wrong direction | Wiring | Set invertDirection or swap wires |
| Servo jitters | Power issues | Use separate servo power supply |
| Stepper skips steps | Speed too high | Reduce maxSpeed |
| Timeout stops motor | Safety feature | Increase timeout or send commands faster |
Debugging
// Enable actuator debugging
qSetMessagePattern("[%{type}] %{message}");
QLoggingCategory::setFilterRules("octomy.actuator.debug=true");
// Check actuator state
for (int i = 0; i < actuatorSet.count(); i++) {
auto& a = actuatorSet[i];
qDebug() << "Actuator" << a.id << a.name
<< "enabled:" << (a.flags & ACTUATOR_ENABLED)
<< "value:" << a.state.currentValue;
}